In the treatment of a golfer's elbow, the rest that the sick hand needs is crucial, so it must be relieved. It is not about immobilization and resignation from being active - quite the contrary. However, it is important to perform certain activities correctly so as not to strain the diseased hand. In this case, you can use special bands or orthoses. Treatment of golfer's elbow is based on eliminating pain and reducing inflammation.
In this case, shock wave therapy works perfectly, as it has an excellent anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, often 5-6 short treatments are enough for the patient to feel a clear improvement. In addition to shockwave therapy for golfer's elbow, physical therapy, stretching and strengthening exercises are also performed. After the exercises, it is recommended to massage the affected area and the surrounding area with ice.
Causes golfer's elbow
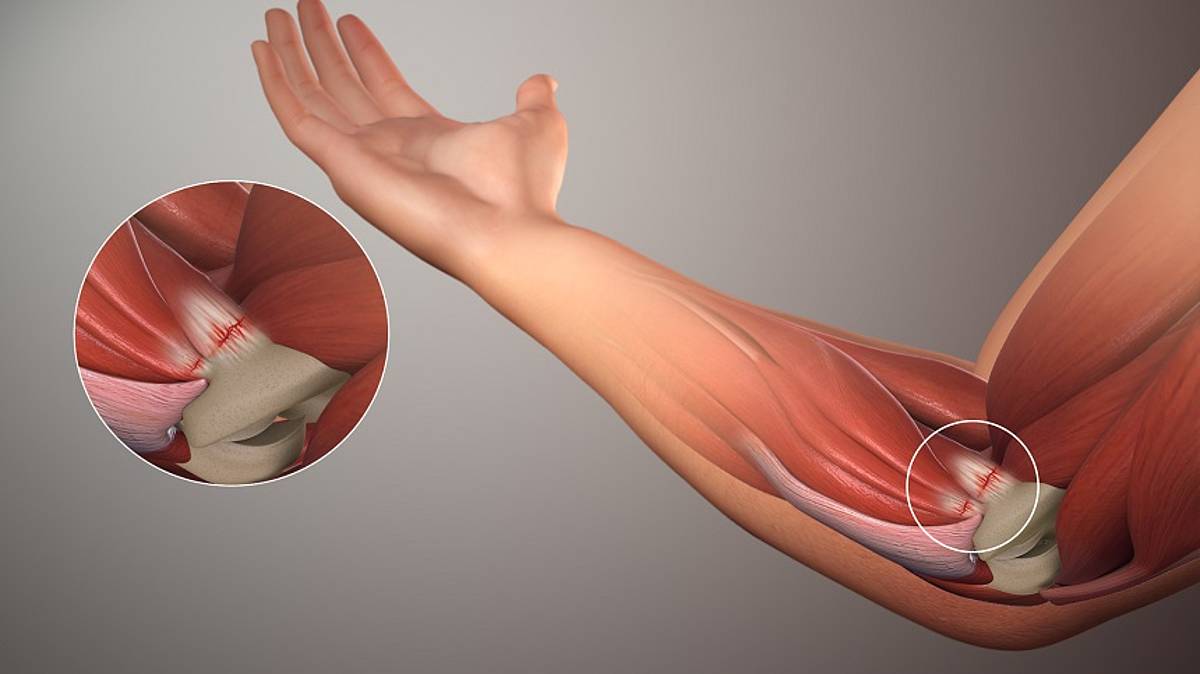
Golfer's elbow is a condition affecting the inside of the elbow. The disease is associated with overload leading to repeated microtraumas, and thus degeneration of the wrist flexors as a result of the constant bending movements of the wrist against resistance. Inflammation develops in the area of the initial attachments of the wrist flexor muscles, which are located on the medial epicondyle of the humerus, there is also pain. The elbow of a golfer is generally complained of by men working as grinders, carpenters, mechanics, office workers, as well as badminton and squash players, as well as rowers and archers, as well as bodybuilders.
Golfer's elbow treatment
The most common complaints about golfer's elbow are pain in the medial epicondyle of the humerus and pain that radiates down the arm when grasping objects and bending the wrist to the elbow. Pain can also be caused by clenching the hand into a fist, as well as pronating the forearm with resistance, and simple activities such as greeting each other with a handshake, carrying groceries or pushing a wheelchair become difficult and painful. Patients suffering from golfer's elbow often complain of a weaker grip.
The severity of the pain depends on the stage of the disease. At the beginning of the symptoms, the pain may be slight and intermittent, felt during specific activities described above. In an advanced state, patients feel pain even while at rest. If untreated, the deteriorating disease may lead to degenerative changes in the elbow joint.




