Treating a tennis elbow with a shock wave is the most effective non-operative technique currently available, and when combined with other methods, it brings clear results. Note, the treatment cannot be combined with steroid injections. If a steroid injection has been performed, the first shock wave treatment is recommended to be performed one month after the injection.
The effects of ESWT (shock wave) are best documented where tissue density changes. For example, where a tendon attaches to a bone (enthesopathies - diseases of the tendons) or the bone attaches to a ligament (desmopathies - diseases of the ligaments). This is why a shock wave is so effective in treating a tennis or golfer's elbow. In addition, the shock wave treatment gives hope to get rid of the pain and eliminates the risk of surgical treatment of this disease, allowing you to return to normal life faster.
.png)
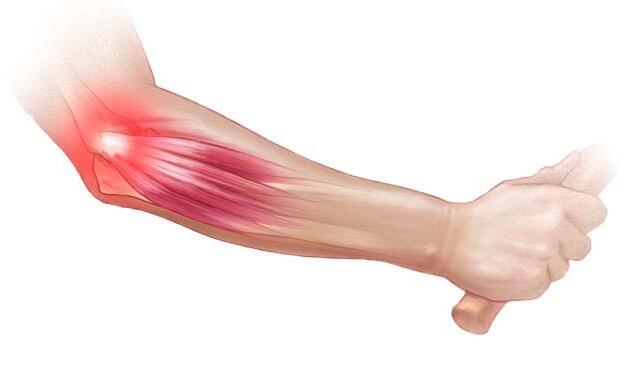
„Tennis elbow”, the so-called enthesopathy is a disease of the extensor muscles of the wrist, located at the site of the proximal attachment. Shock wave therapy with the Rosetta ESWT device is an available and effective method of rehabilitation of ailments.
Tennis elbow - shock wave treatment
Enthesopathy is a condition that occurs most often in the age range of 30-65 years. In tennis practitioners, the cause of the disease is improper backhand exercise. In most patients - 90% - its appearance is in no way related to the game of tennis. The most common causes of complaints are repeated movements of forearm pronation and supination, wrist flexing / extending, and overloading when lifting heavy objects with the palms facing downwards.
Shockwave to tennis elbow:
It affects the tissue:
- Pathologically changed area of the attachment of the tendons of the extensor muscle of the wrist to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
- Reduction in the function of the affected limb (dorsiflexion of the wrist)
- Pain in the area around the outside of the elbow.
Effect of an electromagnetic wave on a tennis elbow:
- Stimulates the tissue of the inflamed tendon to regenerate,
- Reduces pain,
- It causes the correct arrangement of the scar cells in accordance with the course of the tendon, which prevents the recurrence of ailments when the patient returns to normal functioning.




